What are Options
Options are specialized contracts that grant the holder the right (but not the obligation) to buy a financial asset in the future on a specific date and at a predetermined price. Example. How options work Suppose you have bought an option:- its duration is 1 month,
- it gives you a right to buy 1 Bitcoin
- at the price of $30,000.
Options: Key Concepts
- An Underlying Asset — a financial asset whose right to buy or sell is determined by the option. Typically, this is a futures contract. Options can also exist for stocks, currency, or any other asset traded on the exchange.
- A Call Option— an option that grants the right to buy an asset at a specified price in the future.
- A Put Option — an option that grants the right to sell an asset at a specified price in the future.
- The Strike Price — the price at which the option buyer can buy or sell the asset in the future.
- The Premium — the amount the option buyer pays to the option seller.
- The Expiration Date — the period during which the option can be used.
Basic Types of Option Strategies
Here are some of the basic types of option trading strategies:- Call Strategy: buying a call option in anticipation of profiting from an increase in the asset’s price.
- Put Strategy: buying a put option in anticipation of earning from a decline in the asset’s price.
- Insurance Strategy: buying a call option on an asset you already own to protect against a drop in the asset’s price.
- Hedging Strategy: buying a call option on an asset you plan to acquire in the future to protect against an increase in the asset’s price.
- Combination Strategy: simultaneously using two or more options.
How Option Trading Works
Here is how an options board for trading looks like: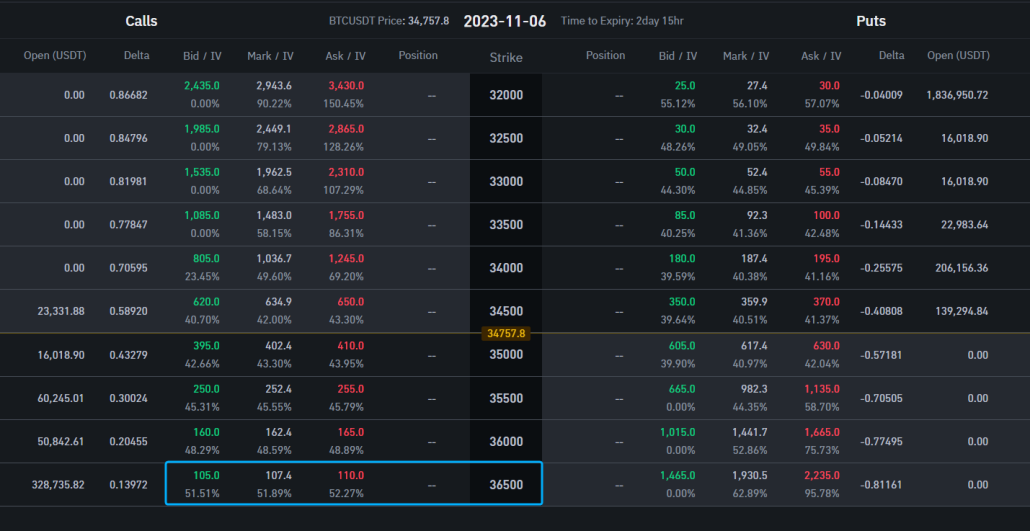
- Options offer the opportunity to profit from price movements of the underlying asset in any direction.
- Options can be used to hedge existing positions (to protect against losses and limit risks). For example, if an investor owns stocks that they believe are overvalued, they can buy a put option to shield themselves from a decline in the stock price.
- Application of various strategies involving 2 options. For example, to profit from market volatility.
FAQ
What are futures and options?
Both financial instruments are derivatives. Their value depends on the underlying asset.
What is the difference between a future and an option?
In a nutshell, a future is an obligation, while an option is a right.
How do options differ from stocks?
Stocks represent the underlying asset, while options are derived from the underlying asset.
What types of options are there?
There are two main types: a Call Option (CALL) allows the purchase of an asset at a predetermined price in the future. A Put Option (PUT) grants the right to sell an asset at a predetermined price in the future.
Which is better – futures or options?
Each of these financial instruments has its own advantages and disadvantages. There is no one-size-fits-all answer. However, futures may be more preferable as they are easier to understand and learn to trade, for instance, through the Market Replay simulator.
Conclusions
Options are a financial instrument with significant advantages but are also quite complex. They are more suitable for developing sophisticated strategies by advanced traders. Futures trading is easier. Moreover, futures traders have an opportunity to analyze cluster charts to have a better understanding of market conditions. Cluster charts are not available for the options market. The ATAS platform provides you with a powerful toolkit for cluster analysis of futures, stocks, and cryptocurrency markets:- clusters can be created on regular timeframes as well as on range charts or charts of other types;
- the list of available indicators and special features is constantly expanding with each ATAS platform update;
- ATAS enables you to load tick data history from futures, stocks, and cryptocurrency markets, providing you with a comprehensive foundation for studying cluster charts;
- The platform offers many other advantages for traders who combine professional-level cluster charts with useful indicators and other features.
Information in this article cannot be perceived as a call for investing or buying/selling of any asset on the exchange. All situations, discussed in the article, are provided with the purpose of getting acquainted with the functionality and advantages of the ATAS platform.





