- First, the asset price falls, creating the illusion of the beginning of a downtrend. Traders anticipating further decline rush to sell the asset, becoming bears.
- However, shortly after, the price begins to rise. This usually happens very rapidly, leaving those traders locked in losses.
What Is a Bear Trap in Trading and Why Does It Occur?
A bear trap in trading is a false downward move that tricks market participants (usually impulsive or less experienced) into opening short positions. Bear traps in the stock market typically happen due to a combination of the following factors: ✔ Market sentiment. The urge to profit from falling prices, combined with the fear of losses and impulsive decisions, leads traders to sell their assets. These emotional trades often end up being unprofitable. ✔ Manipulation by major players. It is possible that market makers or large investors intentionally drive the price down to trigger mass selling by retail traders, only to buy the assets back at a lower price. ✔ Technical factors. False breakouts of support levels or misleading signals from indicators can trick traders into thinking a downtrend will continue. ✔ Fundamental factors. Short-term panic triggered by news or rumors can cause temporary drops, followed by a quick recovery once the news is fully absorbed.Examples of a Bear Trap
Bear traps occur quite frequently in the stock market, both intraday and on higher timeframes. Example 1: A bear trap in the e-mini S&P 500 futures market on a 3-minute timeframe: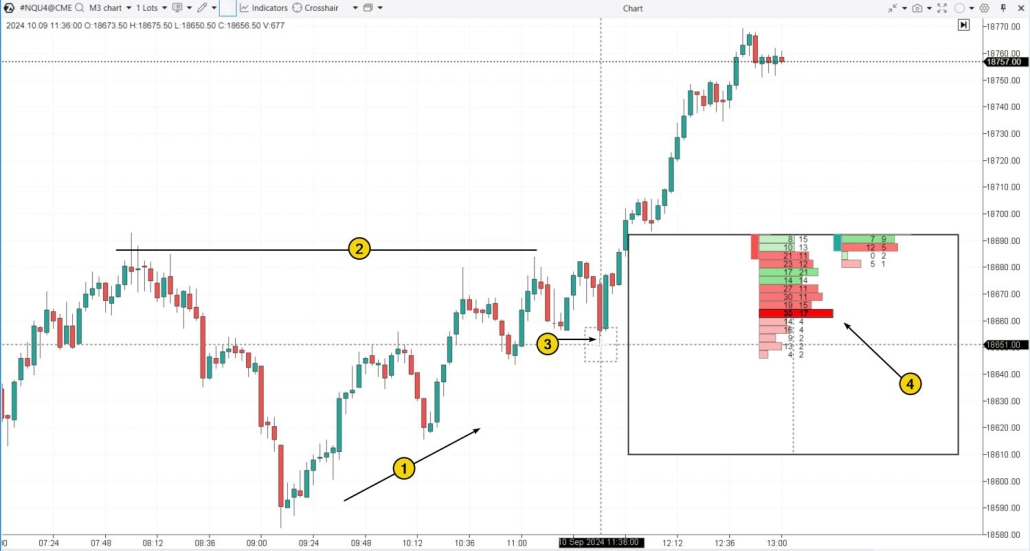
How to Spot a Bear Trap – Technical Analysis
A bear trap on the chart is usually identified by a breakout of a support level. This typically happens in the following way:- Entering the bear trap. The price briefly drops below a clearly visible trendline, a previous low, or a psychological price level. This prompts market participants to open short positions( and close their long positions, either manually or through stop-loss orders).
- Closing the trap. Instead of continuing to fall, the price unexpectedly reverses and starts to rise. This often happens quickly to limit the chances for bears to exit without taking a loss.
Bear Trap Patterns
A key element in trading bear traps is understanding the context. The most relevant situations for bear traps to form include:- Breaking out of a notable range. In this scenario, traders who mistakenly believe a bearish breakout is genuine can easily fall into the trap.
- A false breakout of a psychological support level. Traders might think that if the price drops below $100, it will continue to slide down to $90 or at least to $95.
- A bear trap in an uptrend. This type of trap aims to create doubt among some traders about whether the price will keep rising, leading them to sell their positions. Often, these positions are then scooped up by more experienced and patient traders.
- Fundamental events. Volatility spikes that come with the release of important news can create ideal conditions for traps to form. During these times, it is hard for traders to objectively evaluate the credibility of rumors and the impact of new information, resulting in significant price movements.
Pattern #1. Slamming in the Gap
The example below illustrates how a bear trap is closed with a wide gap on the cluster chart for AAPL stock on a daily timeframe.
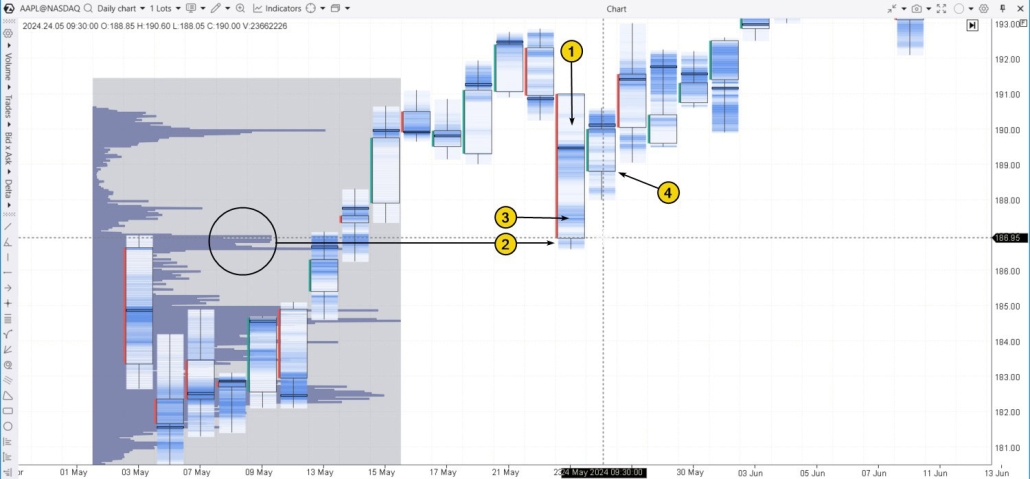
Pattern #2. False Breakout from a Range
When the price of a financial asset moves within a range, it creates a tricky situation for trend traders, who might mistakenly interpret a price movement as a breakout in one direction. An example on the Litecoin chart, where the added Delta indicator helps confirm the market sell activity with spikes of negative values.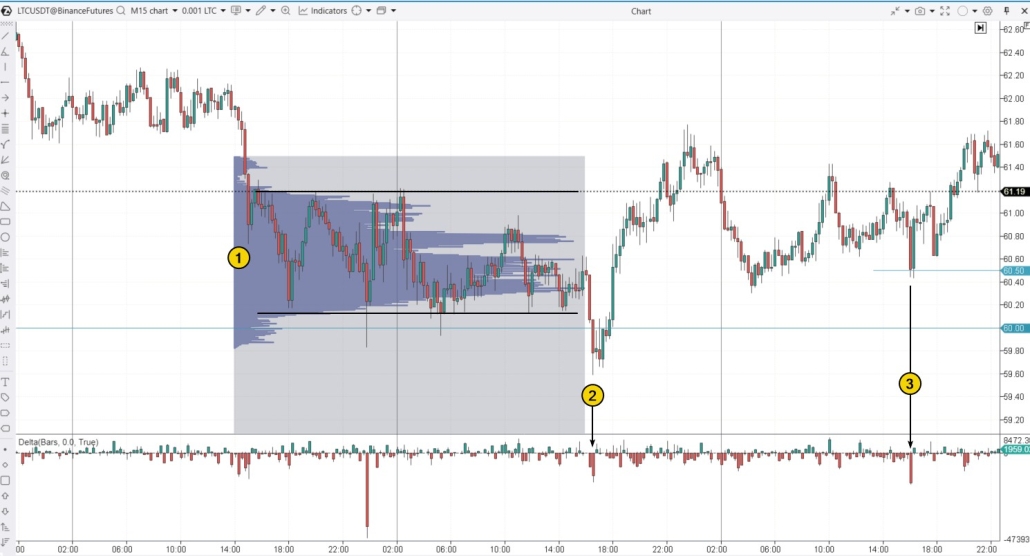
Pattern #3. Bear Trap at the End of Accumulation
Accumulation, a term from Richard Wyckoff’s methodology, refers to a phase (highlighted in purple below) when the market is sluggish, and large players are quietly accumulating assets at low prices, preparing for a future price rally. Wyckoff called bear traps at the end of accumulation phases terminal shakeouts. Example. Microsoft (MSFT) Stock Chart 2022 was a tough year for the stock market, with rising inflation, recession fears, and other challenges. This is reflected in the direction of the 100-period Exponential Moving Average (EMA).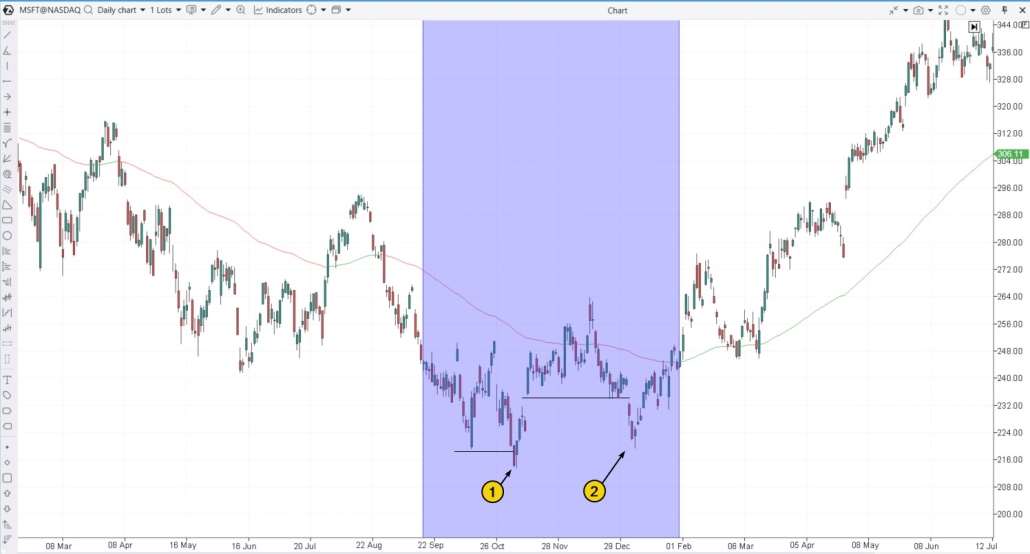
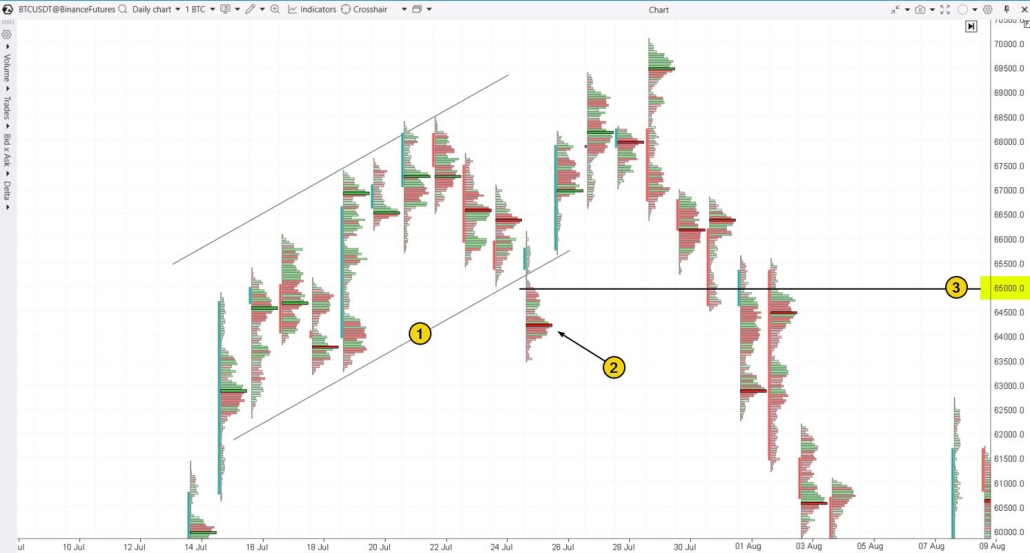
Pattern #4. A Bear Trap In an Uptrend
In a rising market, bear traps often lead to a transfer of contracts from traders expecting a reversal to those betting on the continuation of the bullish trend. Example. The chart below shows a cryptocurrency asset that, at the time of writing, was experiencing a wave of hype. The green line in the lower right corner is the moving average, signaling the continuation of the uptrend as the price broke above the key psychological level of 0.19000.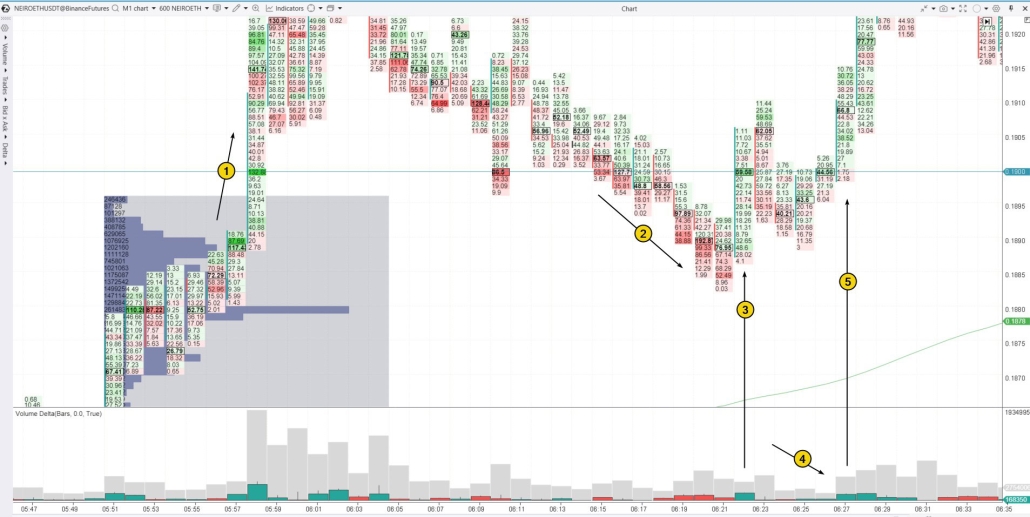
- some traders thought the “pump” was over and a “dump” was about to begin;
- others were closing their long positions (for example, those who had bought around the profile bulge before the 0.19 breakout might have exited near breakeven).
Pattern #5. Bear Trap Driven by News
September 11, 2024, was a key day due to the release of the Consumer Price Index (CPI). Inflation was a hot topic at the time, as traders were anticipating a possible rate cut from the Federal Reserve.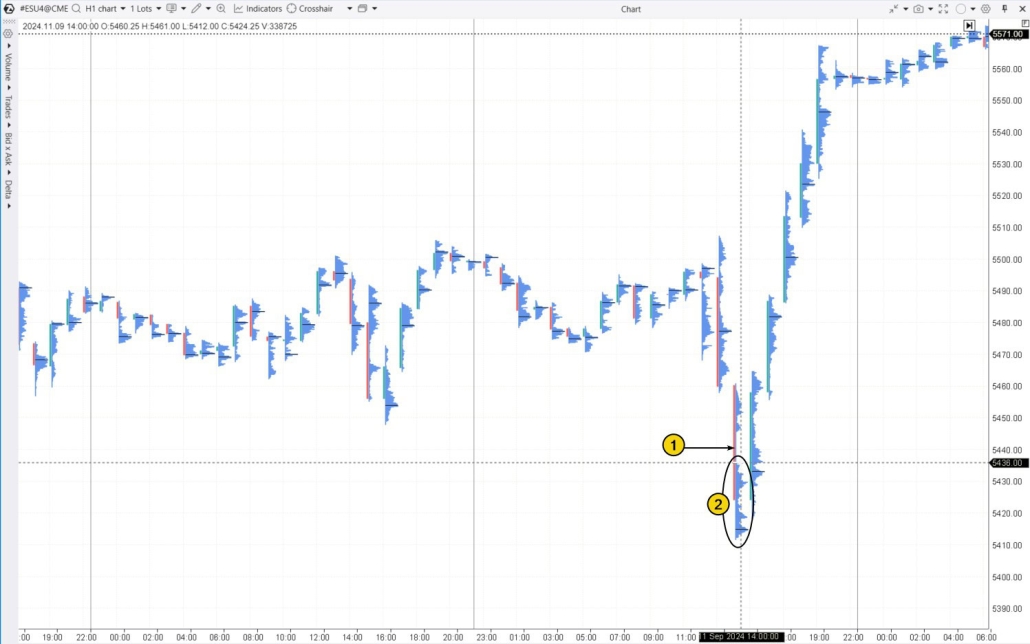
Pattern #6. Bear Trap Near a Psychological Level
The cryptocurrency market is characterized not only by volatility but also by traders’ emotional reactions. Traps around round-number levels are noticeable on the daily charts of nearly any crypto asset. Example. A daily footprint chart of Litecoin with the Round Numbers indicator added.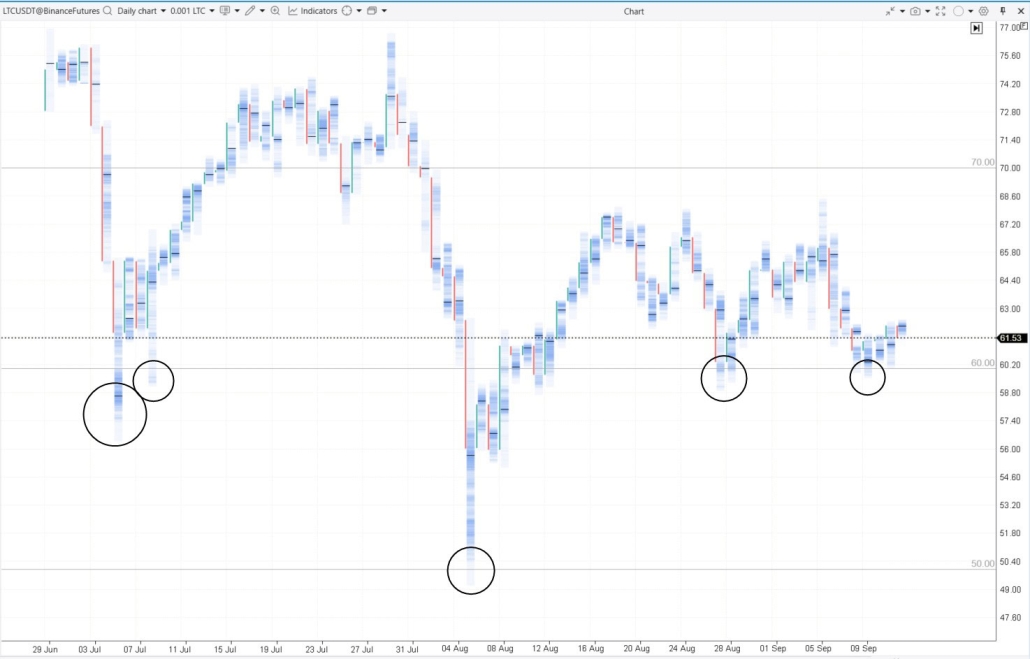
How to Trade the Bear Trap Pattern: The Best Strategies
A bear trap is based on the principle of “one trader’s loss is another’s gain.” It prompts less experienced traders to sell off their assets during a deceptive price drop, creating opportunities for more skilled and informed participants to profit. To effectively trade bear traps, it is important to understand how and at whose expense the profit is generated.Strategy #1. Buying Above the Trap’s Bulge
Let’s say you have identified an important support level, and a false breakout of this level could lead to the formation of a bear trap in trading. What comes next? Let’s look at this more aggressive approach on the chart. Example. Throughout the day, the price remained above the level (1), forming higher highs. But during a volatile U.S. session, it briefly dipped below, likely triggering a wave of sell orders. This, in turn, set the stage for a bear trap.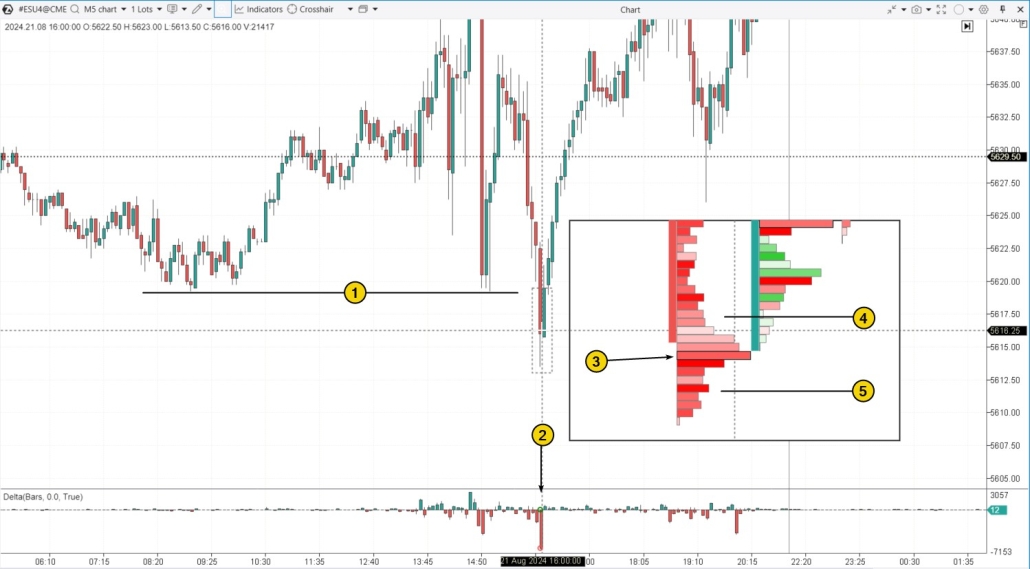
- a surge in negative delta (2);
- a red-colored bulge on the profile (3), showing significant market sell orders;
- the price holding above this bulge. If these mass market-sell orders were causing real selling pressure, the price would likely fall below those large red clusters.
Strategy #2. Trading on the Exit of the Trap
To implement this more conservative strategy, it is important to wait for buyers to step in and close the bear trap. Example. This Bitcoin volume chart visually highlights the delta percentage within the total volume of each candle.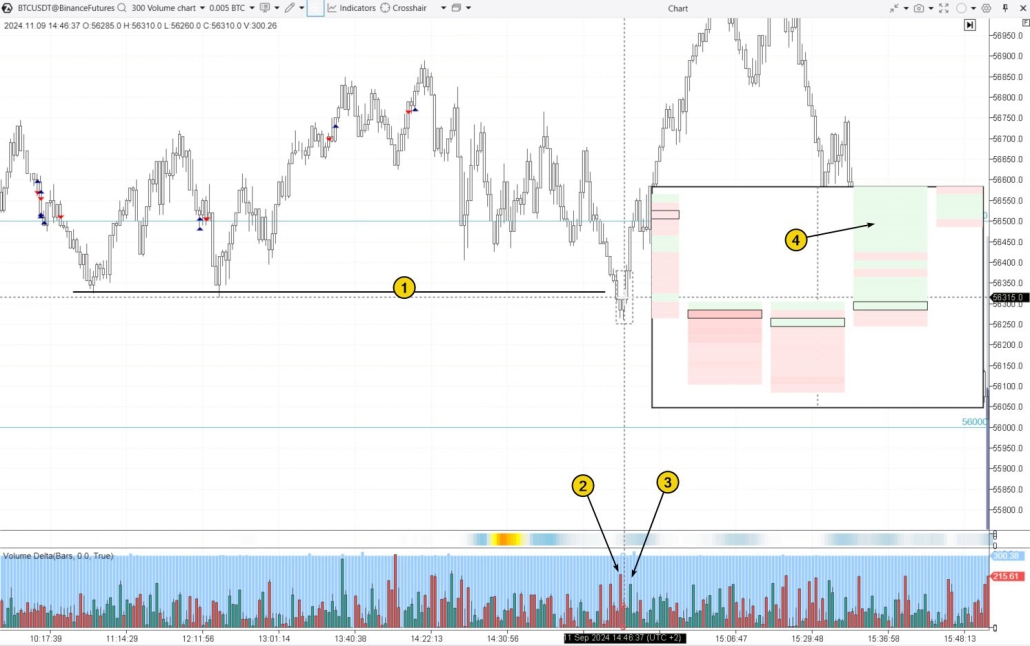
Why Do You Need to Avoid the Bear Trap and How Do You Do It?
It is important to avoid bear traps to prevent losses during a false breakout, when the price suddenly reverses upward after a short-term drop. Traders caught in such a trap may sell their assets at the low and experience psychological discomfort as they watch the price rise afterward. There is no foolproof method to completely protect yourself from losses in trading, including losses from bear traps. Therefore, it is crucial to always manage risk: set reasonable stop-losses and avoid risking too much of your capital on a single trade.Context Analysis
Monitor multiple timeframes, study the strength of trends, and identify key support and resistance levels to get a broader picture of the market. This will help you understand whether the current market situation is vulnerable to bears.Analyzing Footprint Patterns
Avoid making impulsive decisions based on a single breakout. Seek additional confirmation through a retest of the level or advanced technical indicators, such as volume indicators (delta) or footprint chart patterns.Become a Market Psychologist
Understanding that the majority of retail traders often act out of fear and greed can help you stay calm during short-term price drops. Traders who grasp how others react to false breakouts of support levels are able to make decisions with a cooler head.How to Trade Bear Traps Profitably?
Use the Market Replay trading simulator. This module of the ATAS platform uses historical data to recreate real-time trading conditions. You can enhance your trading skills, especially in identifying bear traps. The training simulates real-world conditions without financial risk, enabling you to learn how to use footprint charts. To try the simulator, download the ATAS platform for free, install, and launch it, and then: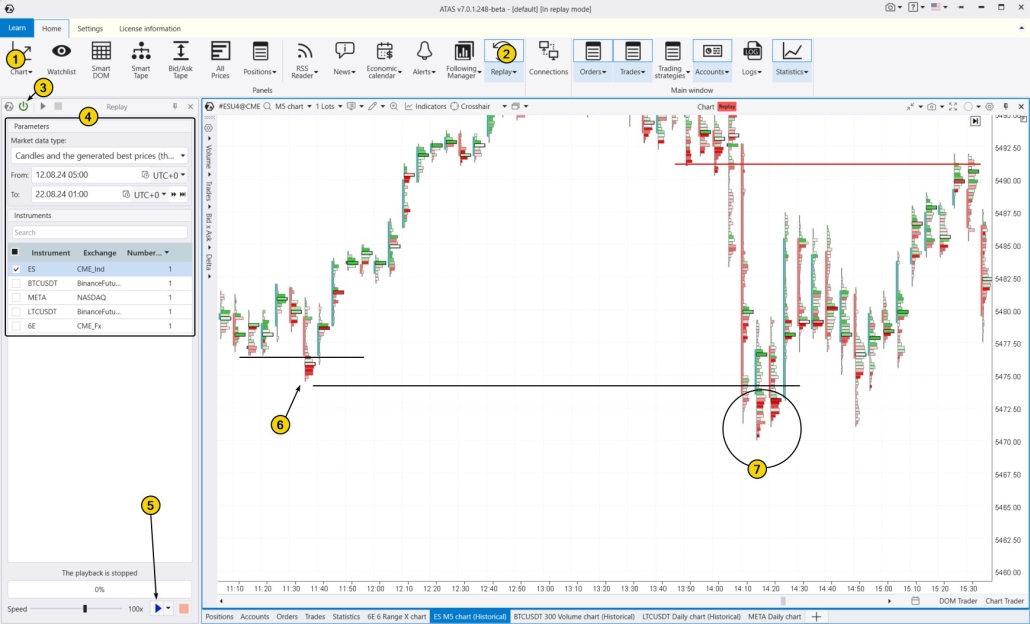
- use Chart Trader and other features to trade on the built-in demo Replay account and then analyze your performance;
- adjust the playback speed, and pause;
- analyze footprint charts;
- use more than 400 indicators;
- use drawing objects, for example, mark support and resistance levels;
- use various chart types (e.g., non-standard Range XV);
- use exit strategies;
- do much more to learn how to profit from situations where others make mistakes.
Conclusions
Bear traps are a key feature of market trading, where most participants end up facing losses, as highlighted by reports from the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA). These traps form due to common psychological patterns among retail investors, who often find themselves on the wrong side of the market. Their selling can inadvertently help professional traders establish long positions at market lows. By using volume analysis tools such as cluster charts (footprint), the Delta indicator, the Market Profile indicator, and others, traders can spot moments when sellers are opening positions en masse during false price declines, making them vulnerable to sharp upward reversals. Download ATAS. It is free. Once you install the platform, you will automatically get the free START plan, which includes cryptocurrency trading and basic features. You can use this plan for as long as you like before deciding to upgrade to a more advanced plan for additional ATAS tools. You can also activate the Free Trial at any time, giving you 14 days of full access to all the platform’s features. This trial allows you to explore the benefits of higher-tier plans and make a well-informed purchasing decision. Do not miss the next article on our blog. Subscribe to our YouTube channel, follow us on Facebook, Instagram, Telegram or X, where we publish the latest ATAS news. Share life hacks and seek advice from other traders in the Telegram group @ATAS_Discussions.Information in this article cannot be perceived as a call for investing or buying/selling of any asset on the exchange. All situations, discussed in the article, are provided with the purpose of getting acquainted with the functionality and advantages of the ATAS platform.





