This article is for beginner traders and it explains what types of exchange orders exist. We will also briefly show you how to use the ATAS platform for working with exchange orders.
Read in the article:- What Bids and Asks are. Basics of order matching in the financial market.
- Market orders.
- Limit and stop orders.
- Other order types.
What Bids and Asks are. Basics of order matching in the financial market
Exchange, whether it is a platform for trading cryptocurrencies or CME, is a place where financial commodities and money are exchanged between buyers and sellers. In general, it is like a regular marketplace. However, modern financial exchanges have specific features and a beginner trader can get confused easily. Let’s start with history to try to help them. The picture below shows the NYSE hall in 1924. Trades were executed by voice in those times.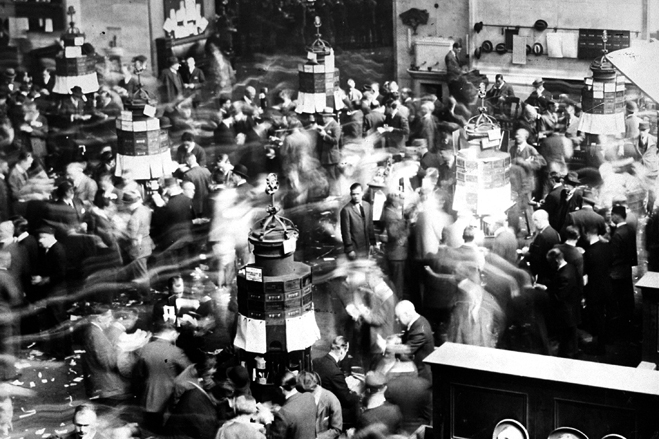
- What a novice should know about order matching.
- ’Good and bad’ order types.
- Order path from creation to execution.
- How to place an order.
- Depth of Market indicator.
- Algorithms of order matching on the CME.
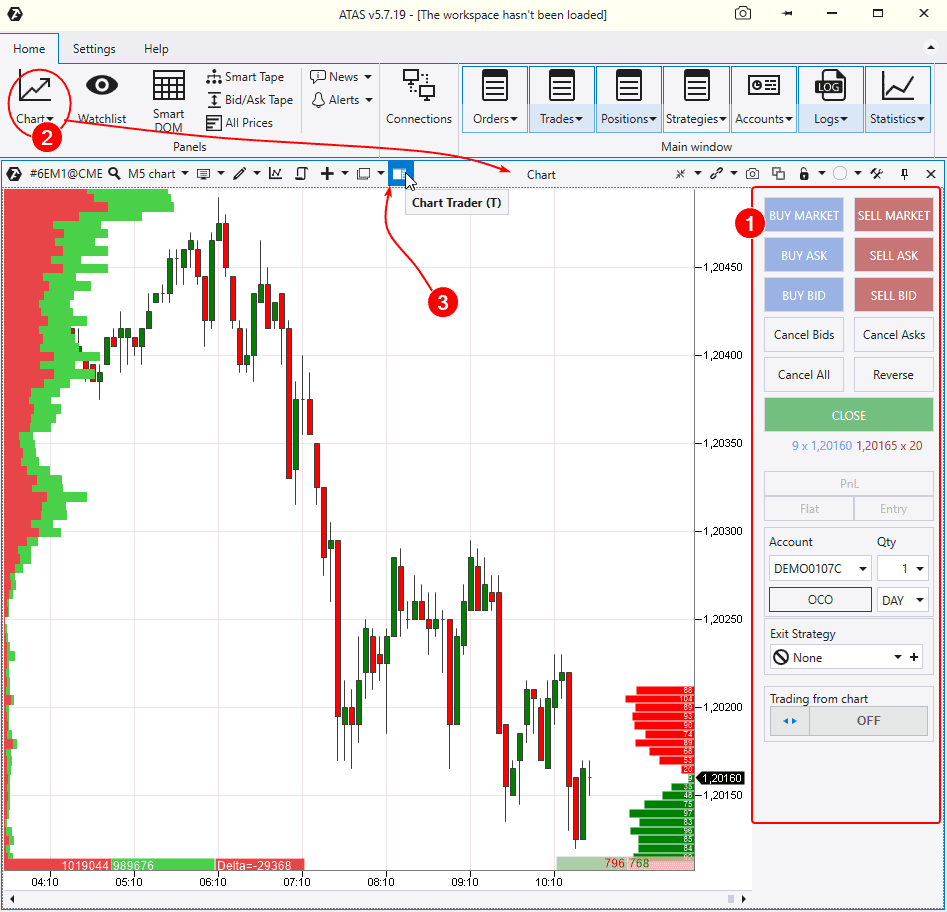
Market orders
What are they? As we have already mentioned, market orders are placed for accepting an available exchange asset buying or selling offer.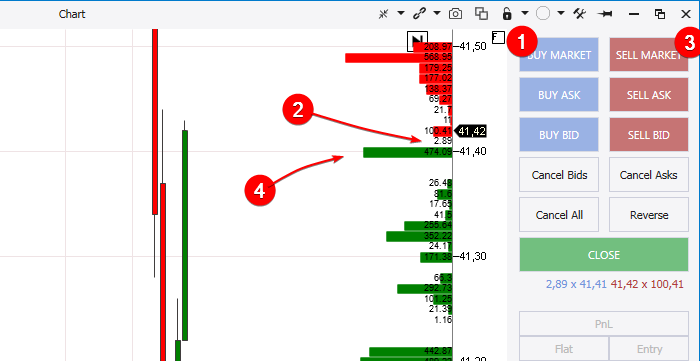
- You send a market order to an exchange for buying an exchange instrument at the best Ask price if you press the Buy Market button (1). Your order will be matched with the lower limit order from the red Best Ask row (2).
- You send a market order to an exchange for selling an exchange instrument at the best Bid price if you press the Sell Market button (3). Your order will be matched with the upper limit order from the green Best Bid row (4).
- the seller cancelled the limit order, which was at the Best Ask price;
- several other market orders from other buyers were placed together with your buy market order and your order was executed after them on the first-come first-served basis;
- the volume in your order was too big and all sell offers at the price of 41.41 and then 41.42 and then even higher were used for executing your order.
Limit orders
What are they? In simple words, these are orders for declaring your intentions. For example, you want to buy an exchange asset but the current price is too high, that is why you place a buy limit order at the price, which suits you. Pros and cons. A pro is that you receive the price you want. A con is that your order may not be executed if the exchange asset doesn’t come back to the price at which you placed your buy order. There can even be a variant when the quotation reaches the level at which you placed the limit order, but you do not enter a trade because there is no offsetting market order for your limit order. When to use limit orders? There is no single answer. Everything depends on your circumstances and specific situation. Let’s consider 4 examples. Example 1. You trade according to the false breakout strategy. It often occurs due to the fact that the cunning market ‘peeps’ into those areas, where multiple stop losses are accumulated. One specific feature of this penetration beyond the local extreme point with the goal to activate stop losses is its short duration. Trying to enter in a position with a market order, you can just miss the point when you can do it, that is why using a limit order will be a more justified decision. Example 2. Placing a take-profit. Example 3. You want to enter the market at a certain price and are ready to stay outside the market if the price doesn’t come back to your order. Example 4. You trade on cryptocurrency exchanges. Commission fees in their systems are usually calculated by taking into account types of orders, which traders use. In terms of cryptocurrency exchange terminology, a maker (who adds his limit order in the general order book) and taker (who withdraws a limit order from the order book using his market order) take part in every trade. So, makers receive a bonus. Exchanges stimulate increase of liquidity on their platforms by reducing maker commission fees. The Buy Bid and Sell Ask buttons (1 and 2) in the Chart Trader panel will serve cryptocurrency traders under such circumstances.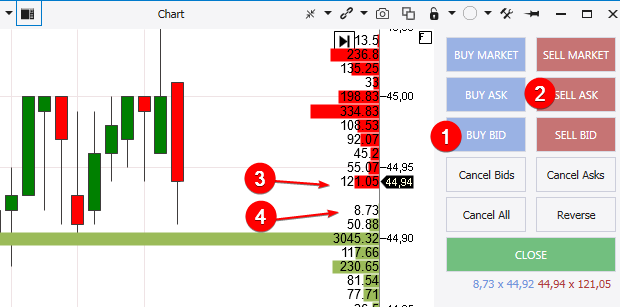
How to place a limit order at a random level?
There are 2 ways to do it:| Below the current price | Above the current price | |
| Buy | Limit | Stop order |
| Sell | Stop order | Limit |
What other orders exist
Pending orders. It is a common name for limit and stop orders. The term ‘pending’ means that sending orders to the exchange is pending until the conditions are met. OCO orders. OCO means One Cancels the Other. It is a combination of two orders. For example, you place a stop loss and take profit when you are in a position. The other order is cancelled after one is activated. Find more details about this combination in the video about protective strategies on our YouTube channel. Do not forget to subscribe! Iceberg orders. These are big orders of professional market participants, which can be split into several small ones. Other market participants may not see them or they can see only parts of them. A trader will have to pay an additional commission fee for using iceberg orders, but it can be justified since iceberg orders allow to hide his intentions. If you still have questions about order types, you can ask them in the comments.Conclusions
What orders to trade? What orders are better and what are worse? There is no simple answer. You need to select orders individually depending on your strategy, market context and other circumstances. Each order type serves its purpose, that is why understanding of specific features of each type allows you to implement your trading ideas in the best way possible. We recommend that you read the Getting acquainted with ATAS. Trading opportunities article to get acquainted with all opportunities for trading from the ATAS platform. It contains a video, which shows various ways of placing orders. Perhaps, the Market auction theory article can be interesting for you if you study order types to understand the exchange trading process mechanics.Information in this article cannot be perceived as a call for investing or buying/selling of any asset on the exchange. All situations, discussed in the article, are provided with the purpose of getting acquainted with the functionality and advantages of the ATAS platform.





