What you need to know about the Japanese yen
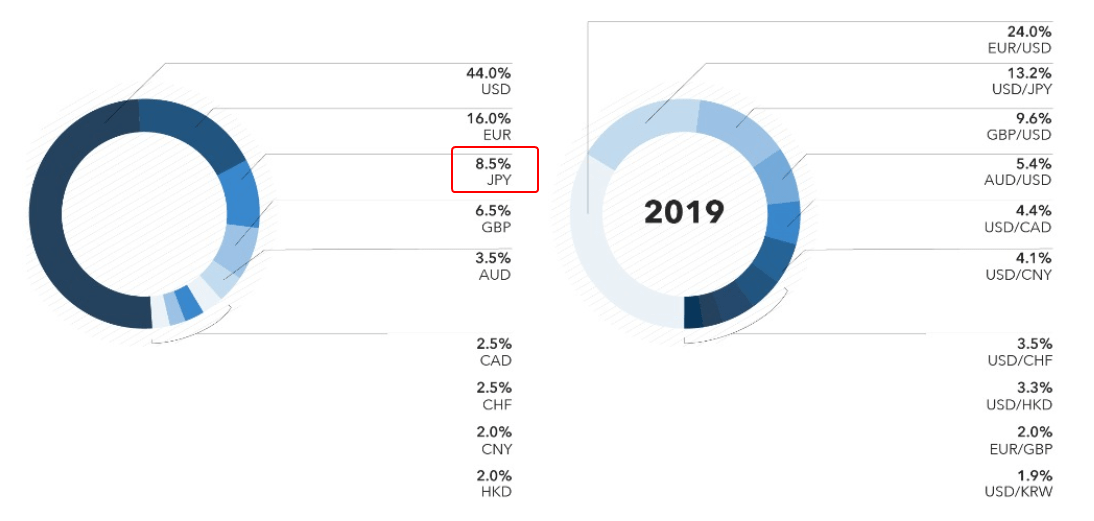
Japanese Yen is one of the six reserve currencies of the world and it takes 8.5% of the trading volume in the Forex market.
Due to the fact that the economy of the Land of the Rising Sun is consistently among the five biggest economies of the world, it has an exceptionally big significance for world trade. Investors also use it as a protective asset, since it is known for its stability in the times of global recessions.
In this article, we will speak about the history of Japanese Yen, its current position in the world of finance and will try to make a forecast whether it makes sense to buy it during the 2020 crisis.
Read in this article:
- Japanese Yen history.
- World trade currency and protective asset.
- Does it make sense to buy Japanese Yen during the coronavirus pandemic?
- Where you can buy and sell Yen.
Japanese Yen history
A specific monetary system named Tokugawa was in Japan from 1603 until 1869. Many local feudals had the right to mint their own coins. In total, there were 1694 different ‘currencies’ in circulation. Of course, such a situation didn’t facilitate economic development. Nothing pointed to the future glory of the Land of the Rising Sun at that time – it was a disjointed and backward agricultural peripheral country.
Large-scale political and economic reforms had started by 1868 in Japan. They laid the foundation of the current industrial power. Experience of the superpower of that time – the Great Britain – was taken as the basis for the reforms.
The renewed centralized state needed a common currency. The history of Yen, as the main Japanese currency, started in 1871 as the result of the monetary reform. The Yen name originates from its form – the coin was round, which sounds in Japanese as ‘en’.
The new currency was set equal to 1.5 grams of pure gold and 24.3 grams of pure silver. It means that the banknotes could have been exchanged to the respective amount of precious metals.
The gold standard was cancelled in Japan in 1933 and the Yen exchange rate was linked, for the first time, to the US Dollar in relation 4.2675 JPY to 1 USD.
The modern stage of development of JPY started in 1953, when it was recognized by the IMF as one of the world currencies. It ceased to be linked to USD in 1973 and became a freely convertible currency.
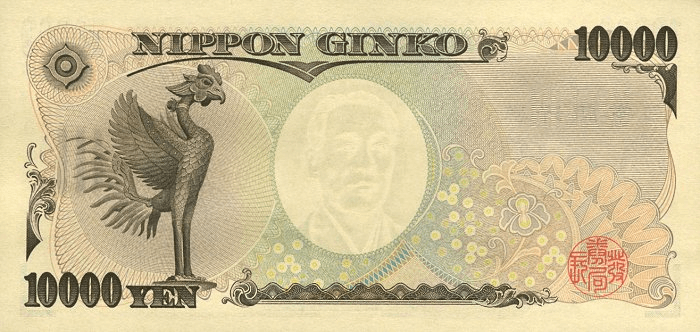
As of now, banknotes of JPY 1,000, 2,000, 5,000 and 10,000 denominations, issued in 2004, are in circulation. The obverse of the JPY 10,000 banknote shows the philosopher and teacher Fukuzawa Yukichi (1835-1901), while the reverse shows the Phoenix statue from the Byodo-in temple.
There are also coins of JPY 1, 5, 10, 50, 100 and 500 denominations in circulation.
World trade currency and protective asset
The Yen code in the international currency market is JPY, which corresponds to the numeric value of 392. The visual currency symbol is also well-known in the form of the letter ‘Y’ crossed by two horizontal lines.
Yen is in the group of six main world currencies on Forex and it accounts for 8.5% of the whole trading volume. It could be compared by its significance for world trade with USD, EUR and GBP. The currency pairs with JPY accounted for 16.8% of the total volume of trades in 2019, which puts it in third place.
Yen is an important world reserve currency. Central banks of other countries, international financial organizations and investment funds purchase it. It accounted for 4% of the total volume of the world reserves in 2014, trailing only USD (63.1%) and EUR (22.1%).
The Japanese currency is considered to be one of the strongest currencies of the world. Thus, during the period from 1949 until April 2020 Yen experienced several cycles of strengthening with respect to USD from 1-to-360 to 1-to-107 (as of April 2020).
This state of things was caused by a strong growth of the economy of Japan after the Second World War and its orientation at international trade. The country is one of the world leading exporters of cars, equipment, electric engineering equipment, ships and various high-technology components.
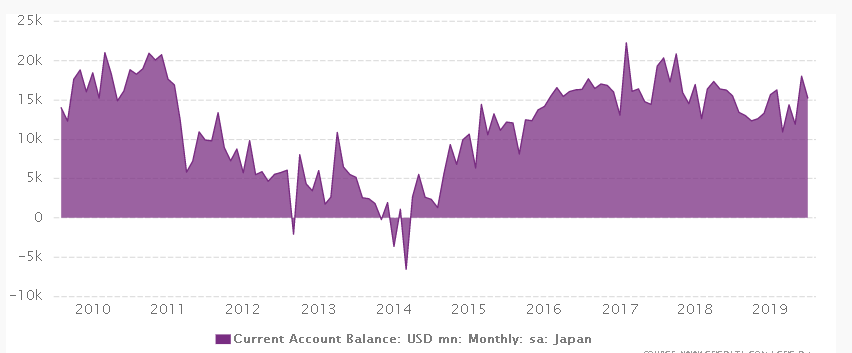
Japanese economy is the third largest economy in the world by GDP volume and Yen systematically strengthens due to a consistently high balance of the current account (see picture below). It means that the inflow of currency into the country is consistently bigger than the outflow, which allows formation of a huge investment resource. Japanese companies are ones of the most active investors in the world due to the massive revenues from export. They actively develop production in the US, China, Germany and other countries.
Due to the Yen ability to become stronger in the times of global crises, investors use it as the safe haven currency. They open a currency position directly or buy JPY denominated bonds. As the counterbalance to this tendency, the Government and Bank of Japan undertake extraordinary measures, which should stop revaluation, since strengthening the currency results in a drop of the export revenues of enterprises while expenditures would stay the same. The Japanese NIKKEI stock index often has an inverse correlation with the JPY exchange rate. Stocks go up when JPY goes down and they go down when JPY goes up.
The USD/JPY uptrend is broken down
The economic crisis, caused by the global coronavirus pandemic, again made many investors pay attention to the JPY value forecasts.
And it is not a surprise, since many investors remember events of 2008-2011, when the world was shattered by the financial crisis. The JPY rate, during those three years, strengthened with respect to USD from JPY 110 per USD 1 to JPY 76 to USD 1. The USD devaluation constituted 44% and was stopped only by the beginning of closing up the Quantitative Easing (QE) programs in the United States.
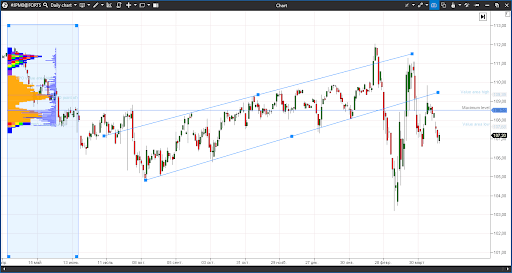
The USD/JPY met the coronavirus pandemic with the USD growth on the daily time-frame. The futures (according to FORTS data), first, jumped up to 112 and then sharply fell to 103.2 during the sharp splash of volatility during the period from the middle of February until March 10. No doubt, stops of very many traders were ‘collected’ there and the trend was broken.
Three consequent peaks in the pair are already below the previous ones. The price consolidated below those levels, at which main volumes had passed. Everything speaks about a good probability of further JPY growth.
The first goal of reduction of the USD/JPY pair (JPY strengthening) are March lows, after breakout of which it makes sense to increase the short position and wait for testing of the 2016 lows in the area of 99.6.
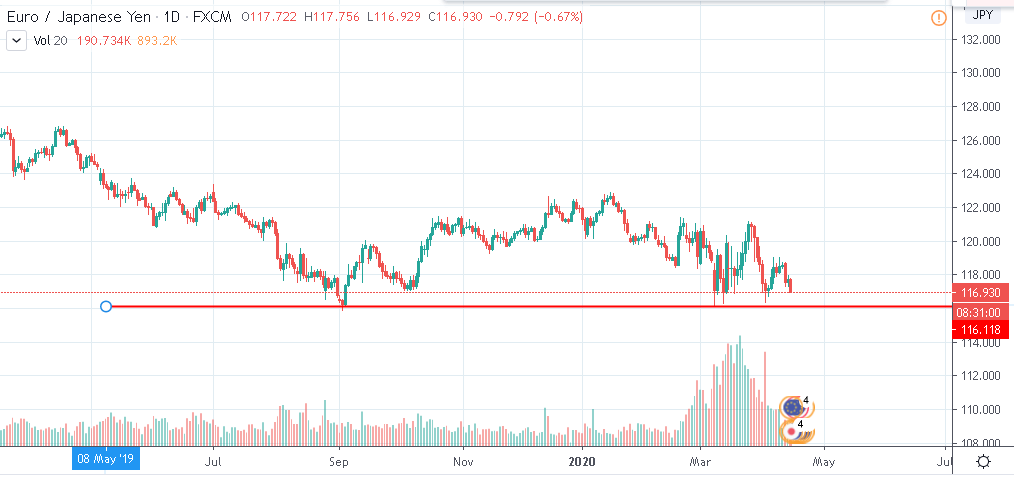
The EUR/JPY rate (Forex) is close again to testing the 116 level, the breakout of which would lead to an accelerated decrease of the European currency.
You may come across the JPY/RUB exchange rate in some trading terminals, however, this pair belongs to exhotic and small-volume ones. Cautious traders shouldn’t put it to the test.
In case you are interested in trading JPY, you may have a look at the JPY futures (6J), which is traded on CME. It could be done through the ATAS platform, but, first, you would need to open a brokerage account.
The JPY index futures contract is also popular among investors. The currency index is a weighted value with respect to other currencies (USD, EUR, CAD, AUD and CHF).
Fundamental analysis of USD/JPY
A number of drivers should be assessed in the fundamental analysis of JPY and forecast of its exchange rate. The following ones play in favour of the JPY exchange rate:
- Many investors consider JPY as the safe haven currency. The crisis aggravation would facilitate an inflow of buyers.
- The United States launched the program of support of the economy by means of emission, the volume of which may exceed USD 5 trillion only in 2020, which would weaken the USD exchange rate.
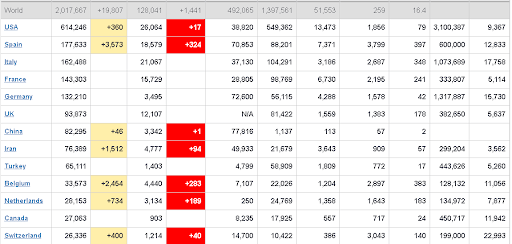
- Japan belongs to the group of countries, which (as of the middle of April) managed to avoid active coronavirus transmission and severe economic collapse. Thus, there were more than 600 thousand infected in the US as of April 15 and more than 100 thousand in each of the major economies of the Eurozone (Germany, France, Italy and Spain). Japan had a little bit more than 8 thousand cases during the same time. The Government managed to bring the worst epidemic scenario under control, which frees its hands for further easing of quarantine measures.
However, there is also unfavourable news for the JPY exchange rate. Thus, the Bank of Japan and Government declared the beginning of the economy support program, which is assessed in USD 1 trillion, on April 7. Taking into account the fact that the country’s economy is not gigantic, this is not a less colossal amount than in the US. Every Japanese family, which would suffer from coronavirus, would get USD 2.7 thousand.
“We decided to allocate JPY 108 trillion for an unprecedented package of measures of support of the economy due to a huge damage from coronavirus”, – explained the Prime Minister Shinzo Abe.
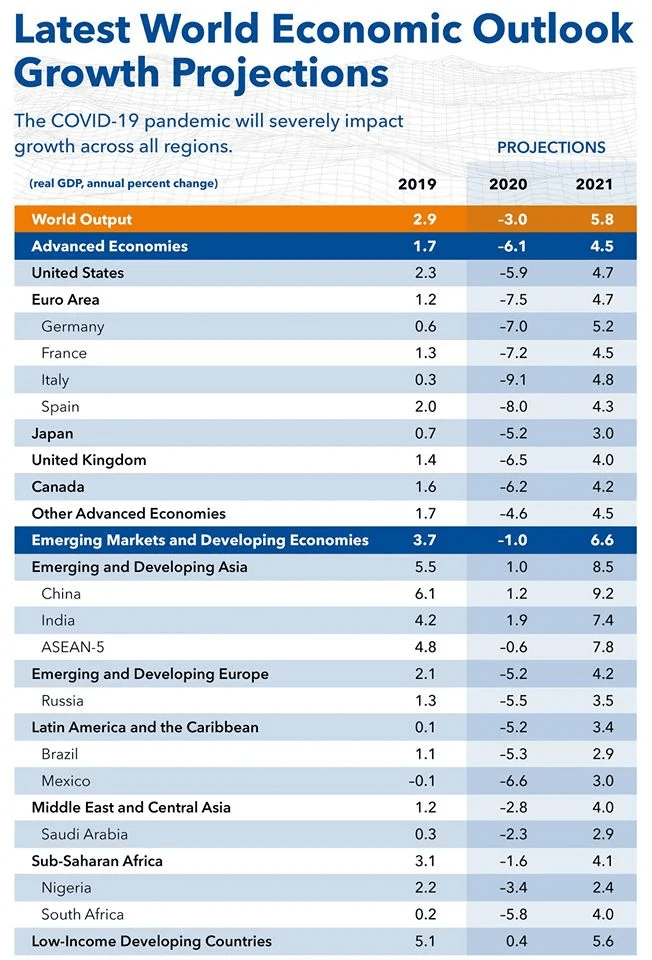
Chances for weakening of the European currency in the EUR/JPY pair are high. The Eurozone economy belongs to the most suffered from the coronavirus pandemic economies, while quarantine measures in the main centers of infection are obviously delayed. According to the IMF, the region’s GDP will fall down in 2020 much stronger that in the majority of countries – by 7.5%, in the US – by 5.9% and In Japan – by 5.2%.
Italy, which anyway is one of the most problematic countries of the region, has suffered from coronavirus more than others. The debt load of this country is extremely high and the rate of growth of the economy had been inactive even before the crisis. This factor creates significant additional risks for the common European currency.
Conclusion
The Japanese Yen is one of the most interesting currencies for trading and investing. It has a significant potential for strengthening in 2020. However, traders should remember that the situation is very unstable in the sensitive currency market. Both new measures (including turning on the printing press) of the Government and Central Bank of Japan and unexpected developments in the coronavirus transmission could shatter the balance of powers.