The pitfalls of Forex trading
The FOREX currency market (FOReign currency EXchange) is the most attractive one for beginners. What is its alternative?
Please, read this article before you start trading on Forex.
Content:
- Forex specific features;
- Forex statistics;
- types of Forex brokers;
- risks of trading through a Forex broker;
- pros of trading currency futures.
Forex specific features
An important feature of trading currency pairs on Forex is absence of a centralised marketplace. Despite the fact that Forex is a huge market, it is loosely regulated because it doesn’t have a managing body, which would control it 24/7.
It would be correct to say that currency exchange is carried out in a decentralized manner in the electronic form on the over-the-counter (OTC) basis. Transactions are performed through computer networks between the market participants all over the world rather than on one centralized exchange.
- Forex is open 24 hours a day 5 days a week. However, some banks trade with each other on weekends.
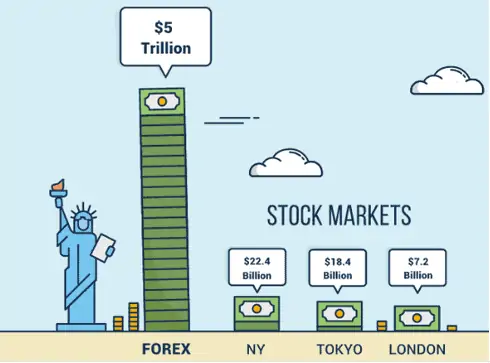
- According to some sources, the Forex trading volume reaches USD 5 trillion a day, surpassing any other stock exchange.
Unlike stock markets, the roots of which go back through the ages (you will find more details in the article about the exchange organizational structure), the modern Forex is a rather young market. It originates from setting up the Bretton Woods system in 1944, when main currencies were allowed to be freely convertible with respect to each other.
Major commercial and investment banks formed Forex at the beginning. They executed trades on behalf of their customers (for example, international manufacturers who wanted to hedge their currency risks) and also realised speculative possibilities for trading currencies on their accounts.
This is ↓ how it looked like in City Corp on Wall Street in 1980:
Internet and personal hardware and online trading operation software capacities were developed in the course of time. And trading on Forex became more easily accessible and popular year after year.
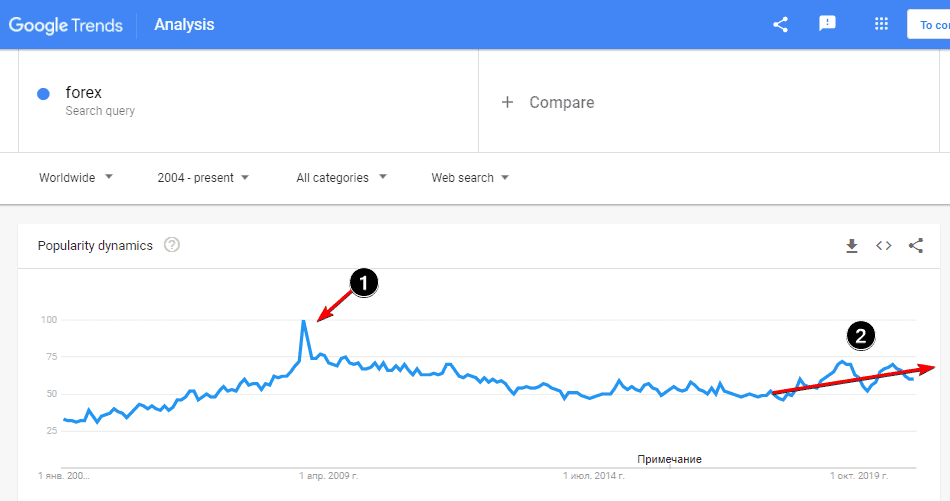
According to the Google Trends statistics (see the picture below), we can see the growing public interest in Forex trading at the very beginning of the 21st century. The highest point of popularity (1) was during the financial crisis in 2008. The interest became to gradually fade out in the 2010s but not strongly (in the trader’s language – within acceptable retracement).
The new round of Forex popularity (2) has been observed during 2019-2020. It is stemming from, among other things, high volatility of currency pairs during the crisis, caused by the coronavirus pandemic.
Demand breeds supply. A whole network of Forex brokers started to develop in response to the public interest. Its core was formed by several dozen famous firms, stocks of which are even traded on NYSE and NASDAQ. Hundreds of small brokers around them ‘come into life’ and ‘die’.
It goes without saying that a man from the street cannot start trading out of the blue along with major banks – UBS, Goldman Sachs, BNP Paribas and others. Forex brokers perform an intermediary function for accessing Forex and focus on small customers (retail traders), whose average deposit is about USD 500-1,000.
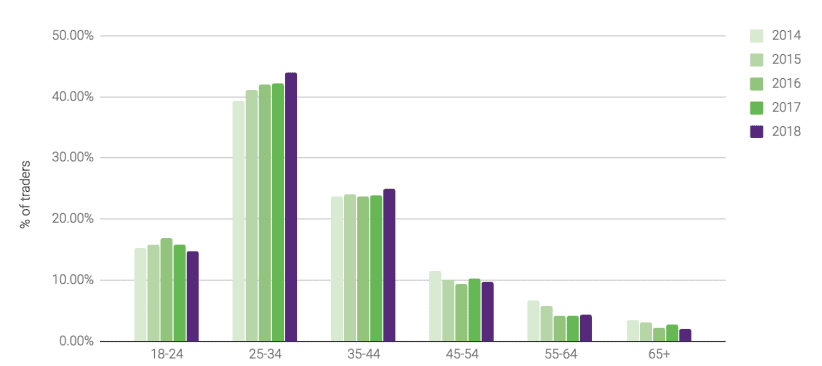
According to BrokerNotes for the year 2018, there were 14 million online traders in the world. The major part of these retailers were young people at the ages from 25 to 35 years.
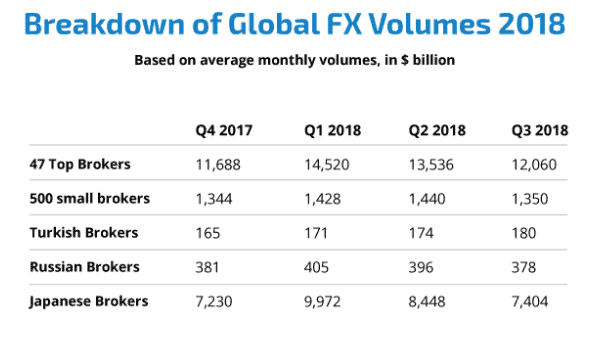
According to Financial Magnates for the same 2018 year, the total turnover of Forex brokers was at the level of USD 15 billion a quarter (which is much less than USD 5 trillion, because Forex brokers provide services to retail traders rather than institutional ones, such as banks and major hedge funds).
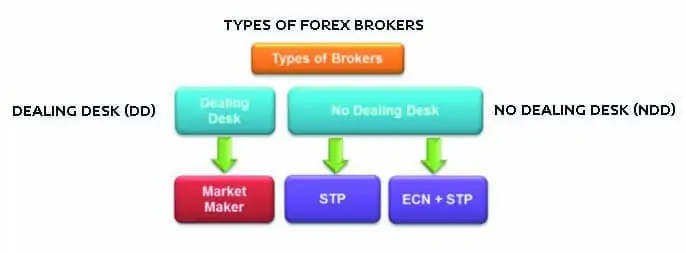
Types of Forex brokers
In fact, a Forex broker is a rather catch-all notion. Dealers are often called brokers, although there is a difference between them.
- Dealers, simply speaking, are firms, which provide quotes from the exchange.
- Brokers provide access to exchange instrument trading.
For the purpose of this article, we will call them all brokers as it is generally accepted. So, depending on availability of a dealing desk (the functionality on providing quotes), there are 2 types of Forex brokers:
- Dealing Desk (DD).
- No Dealing Desk (NDD).
Let’s consider them in more detail.
Type 1. Dealing Desk Forex broker
In this case, a broker can match orders of his customers together. One customer buys EUR/USD and another sells it. The broker executes both orders making money on the commission fee and/or spread.
If an order, which comes from one customer, doesn’t have an offsetting order, which comes from another customer, the broker can:
- Bring the trade to the interbank, where an offsetting order will be found for sure.
- Play the market maker role by himself. In other words, the broker will execute the customer’s order by opening an offsetting order on his own account. If the customer constantly trades in the black, the broker will have accumulated losses. This is how a conflict of interests arises.
Specific features of DD (Dealing Desk) brokers:
- the customers receive quotes from the broker’s server rather than from the interbank;
- fixed spreads are inherent.
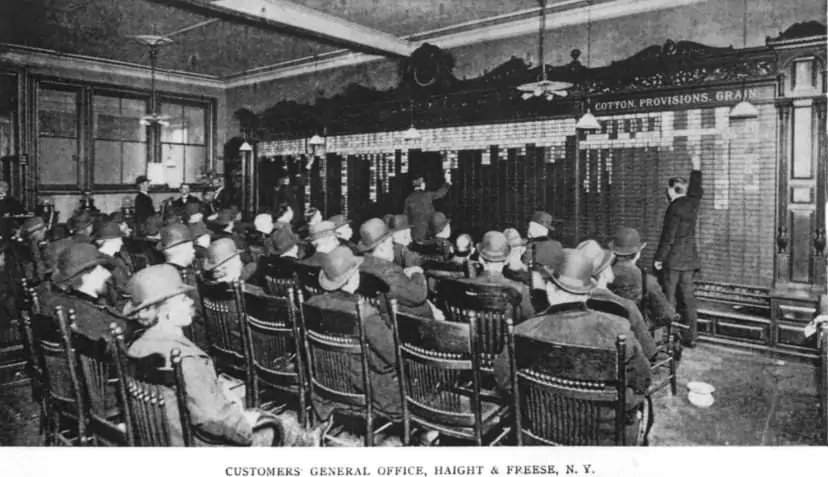
The ‘being own market maker’ scheme of business has been well-known since long ago. Bucket shops flourished in the United States as early as at the end of the 19th century. These were shops where gamblers bet on stock price growth/fall (the photo below shows the Haight & Freese bucket shop in Manhattan in 1899).
Besides, a bucket shop didn’t buy or sold stocks. It just accepted bets also providing leverage. It strongly resembles CFD (Contract For Difference) on stocks of modern Forex brokers. Don’t you think so?
By the way, you can read about bucket shops in the excellent book ‘Reminiscences of a Stock Operator’, written by Edwin Lefevre in 1922. What else a trader could read.
Type 2. No Dealing Desk
Forex brokers without a dealing desk transmit stock quotes from the interbank and deliver their customer trades to the interbank, whereby there are 2 variants: Straight Through Processing (STP) and Electronic Communication Network (ECN). The difference between them lies in their technologies.
| DD | STP | ECN |
Frequently fixed spreads | There could be fixed and floating spreads | Floating spreads |
A broker may trade ‘against a customer’ | Customer orders go to liquidity providers | Orders are executed at the cost of liquidity providers or other ECN participants |
A broker may supply artificial quotes | Quotes come from liquidity providers | Quotes come from liquidity providers and other ECN participants |
Requotes and execution delays are possible | Automatic execution without requotes* | Automatic execution without requotes* |
*- requotes are quote changes during the trade execution. Usually, they are done for the worse of a customer.
Risks of trading through a Forex broker
If a beginner trader opens an account with a Forex broker, he takes not only those risks, which are connected with the currency exchange rate fluctuations, but also takes additional risks, which are connected with the broker’s bad practices.
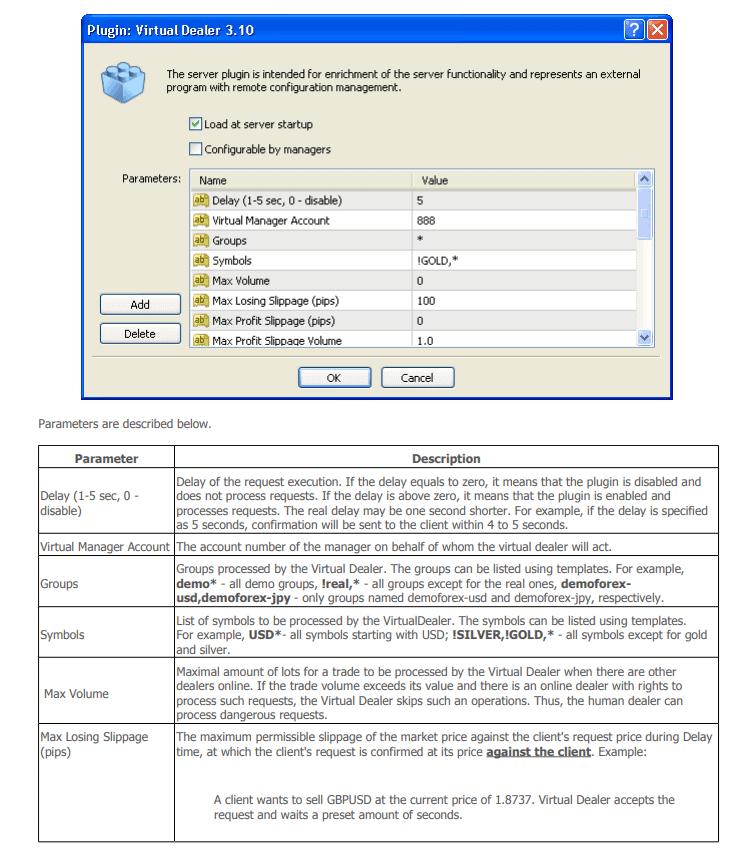
For example, the picture below shows a screenshot of a part of the instruction on setting up the so-called Virtual Trader plugin.
Go and google for it. Many web-sites about Forex say that this plugin is installed on the broker’s server side and allows playing against his customer through his MetaTrader terminal.
We do not have a proof of the identity of this document. It’s up to you whether you believe it or not.
From our side, we can just say that if a broker wants to create some adjustable functionality, in order to ‘throw sand in the wheels’ of a trader, technically it is quite possible.
A question arises – how lawful is it? Why do financial regulators ‘close their eyes to’ broker’s confidence tricks?
The answer is in ‘loyally regulated’ jurisdictions. Web-sites of the agencies, which provide full cycle services, use more eloquent phrases like ‘in the best unregulated jurisdictions’.
Pros of trading currency futures
Let’s assume that you:
- understand that dealing with Forex brokers means additional risks;
- do not want to miss investment/speculative opportunities, offered by currency markets.
What is then?
Take heed of futures markets. For example, the euro futures contract. It is traded on a centralized exchange.
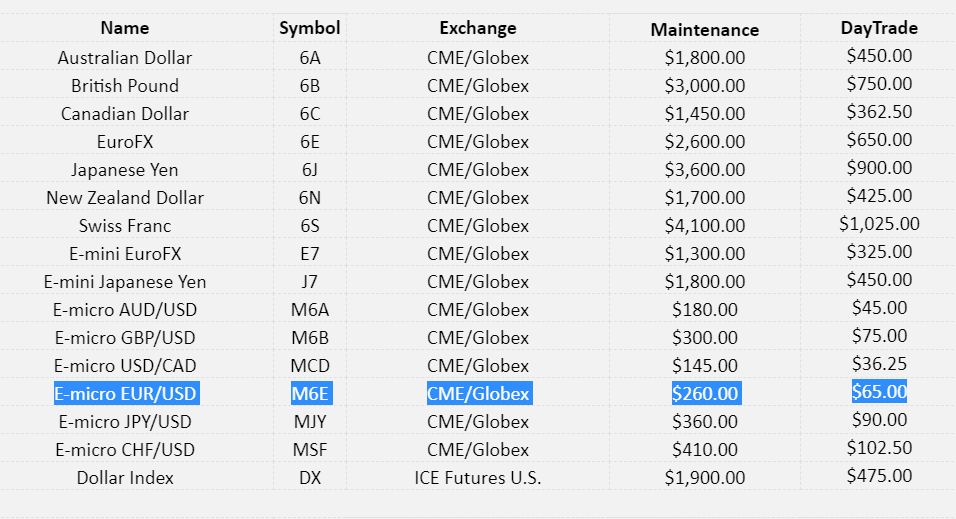
You need to have USD 65 only (according to one popular broker who provides access to the CME forward markets) for buying or selling the E-micro contract during a day. It is not too much. Of course, you will be asked to deposit, most probably, more than USD 65, but it will be reasonably comparable to the deposit on a Forex brokerage account. This is the first pro.
The second pro is regulation
- National Futures Association (NFA, established in 1982);
- Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC, established in 1934);
- Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA, established in 1939);
- and others.
These ↑ US financial market regulators have much more weight and authority than the St. Vincent & Grenadines Financial Services Authority (FSA).
The third pro is transparency
We posted a limit order and it appeared in the order book.
Is it possible to do it on Forex? You may try )
The fourth pro is installation of advanced platforms for analysis and trade
For example, if you trade currency futures through the ATAS platform, you can get a real advantage, using such powerful instruments as:
- Footprint,
- Market Profile,
- smart Volume indicators,
- Smart DOM,
- Smart Tape,
- and others.
Conclusions
This material has no purpose to disrepute:
- MetaQuotes terminal.
- Forex brokers. Some of them are decent companies, which have licenses of reputable regulators and provide high-quality services.
- The Forex in general.
The goal of the article is to help a reader to make an informed decision in order to use available opportunities in the currency markets.
Forex spot | Currency futures | |
Regulation | There is a risk to open an account in an unreliable jurisdiction | Reliable |
Quotes | A broker may manipulate quotes | Come from the exchange |
Accessible for beginning | Yes | Yes |
Using advanced platforms | No | Yes |
If you choose currency futures trading as an alternative to Forex, the ATAS platform will become your reliable assistant in this captivating and potentially profitable business.
Did you like the article? Read an article on the similar subject → American stock indices: micro contracts or CFD.
Information in this article cannot be perceived as a call for investing or buying/selling of any asset on the exchange. All situations, discussed in the article, are provided with the purpose of getting acquainted with the functionality and advantages of the ATAS platform.